Aneurysm Surgery
Brain aneurysm repair is a surgical procedure to correct an aneurysm, a weak area in a blood vessel wall that causes the blood vessel to bulge or balloon out and sometimes burst (rupture). It may cause: Bleeding into an area around the brain (also called a subarachnoid hemorrhage) Bleeding in the brain that forms a collection of blood (hematoma). Brain aneurysm repair by clipping of the aneurysm by surgery is routinely done at Sobti Neuro Hospital using the neurosurgical microscope with the best success rate in North India of more than 95%. The hospital has done around 500 successful brain aneurysm surgeries. The patient goes home walking 3 days after the surgery.
Brain Tumors
A brain tumor is an intracranial solid neoplasm, a tumor (defined as an abnormal growth of cells) within the brain or the central spinal canal. Some tumors are brain cancers. Brain tumors include all tumors inside the human skull (cranium). Surgery for various Brain Tumors is routinely done at Sobti Neuro Hospital. Surgery is the most effective treatment for brain tumors and Sobti Hospital's team of expert neurosurgeons has safely and effectively operated on even the most challenging brain tumors using latest neurosurgical microscope. There are more than 5000 successful cases of brain tumors operated at Sobti Hospital.
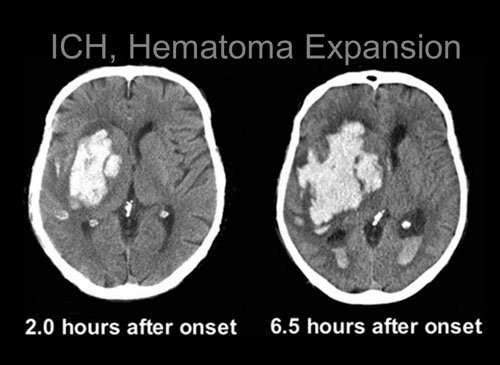
Brain Hemorrhage
The term "brain haemorrhage" means a sudden and spontaneous accumulation of blood in the brain. The symptoms of a brain hemorrhage can vary. They depend on the location of the bleeding, the severity of the bleeding, and the amount of tissue affected. Symptoms may develop suddenly or over time. They may progressively worsen or suddenly appear. Treatment for bleeding in the brain depends on the location, cause, and extent. There are lots of patients with brain hemorrhage coming to Sobti Hospital routinely. The brain hemorrhage is diagnosed immediately and the patients are treated as required both with or without surgery.
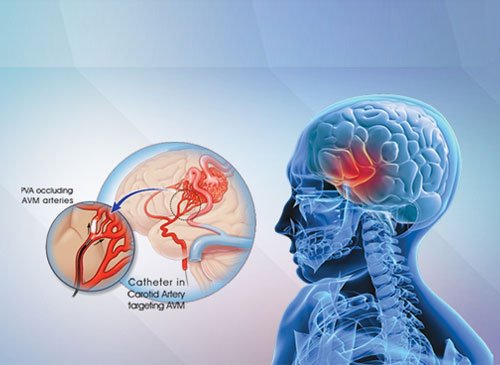
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. AVMs become symptomatic as they can cause intense pain or bleeding in the brain or lead to seizures. Sobti Hospital has treated a good number of patients with AVM in brain who presented with brain haemorrhage or seizures at the hospital. Surgery was done in patients who required it.
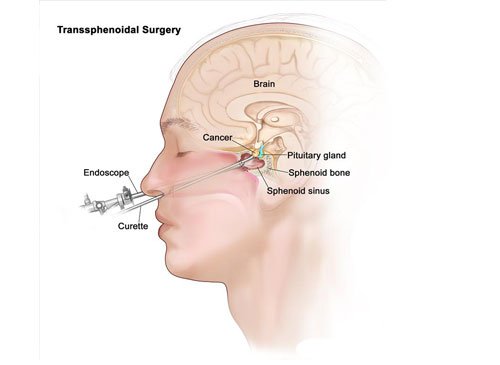
Pituitary Surgery Through Nose
The main treatment for many pituitary tumors is surgery. In this approach, the neurosurgeon at Sobti Hospital makes a small incision under the upper lip and the whole pituitary tumor is removed from the brain using the neurosurgical microscope or endoscope. The hospital has done around 1000 cases of pituitary tumors with a success rate of more than 98%.

Head Injury
The term "brain haemorrhage" means a sudden and spontaneous accumulation of blood in the brain. The symptoms of a brain hemorrhage can vary. They depend on the location of the bleeding, the severity of the bleeding, and the amount of tissue affected. Symptoms may develop suddenly or over time. They may progressively worsen or suddenly appear. Treatment for bleeding in the brain depends on the location, cause, and extent. There are lots of patients with brain hemorrhage coming to Sobti Hospital routinely. The brain hemorrhage is diagnosed immediately and the patients are treated as required both with or without surgery.
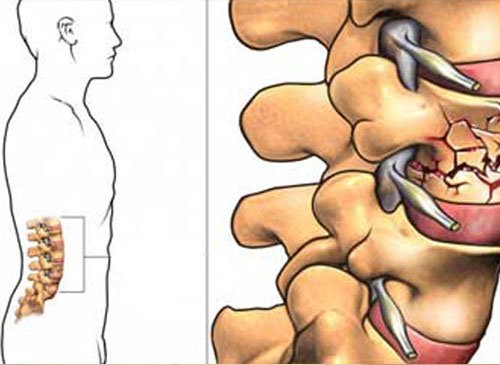
Spine Fractures
Spinal fractures are different than a broken arm or leg. A fracture or dislocation of a vertebra can cause bone fragments to pinch and damage the spinal nerves or spinal cord. Most spinal fractures occur from car accidents, falls, gunshot, or sports. There have been many patients who presented with spine fractures to the hospital. The fracture was stabilized by surgery and the patients recovered very well. When pain from a spine fracture persists, vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty is considered to repair the fracture which is done in conscious state and the patient is discharged the same day.
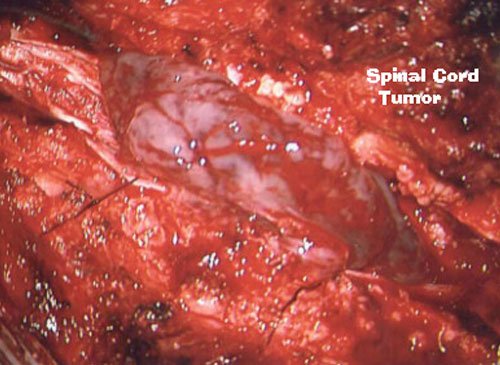
Spinal Tumor
Sobti Neuro Hospital routinely does surgeries of spinal tumours with the neurosurgical microscope. A spinal tumor is a growth of cells (mass) in or surrounding the spinal cord. Surgery is needed to relieve compression on the spinal cord. These tumors are completely removed. The symptoms seen are due to spinal nerve compression and weakening of the vertebral structure. Symptoms of spinal cord compression include weakness in arms and legs, sensory loss, gradual onset paralysis and incontinence of bowel and bladder.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Sobti Neuro Hospital does Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery using the neurosurgical microscope and endoscope. A very small incision is made on the back and the entire surgery and the pathology is treated through it. The patient starts walking on the same day of surgery and is discharged from the hospital. There are lots of patients who have been treated with this technique. MISS is one of the most rapidly advancing surgical procedures. Through highly specialized tools, minimally invasive surgery is an attractive option for patients who want a quicker recovery after surgery, less post-operative pain, and smaller incisions.
Disc Prolapse
A prolapsed disc often causes severe lower back pain. The disc often presses on a nerve root which can cause pain and other symptoms in a leg. In most cases, the symptoms ease off gradually over several weeks. The usual advice is to do bed rest as much as possible. Painkillers may help. Sobti Neuro Hospital has performed more than 5000 successful surgeries of the whole spine. Prolapsed disc surgery ordinarily is performed as a last resort after conservative treatment has failed to help manage neck pain, back pain or other symptoms associated with intervertebral discs that have prolapsed.
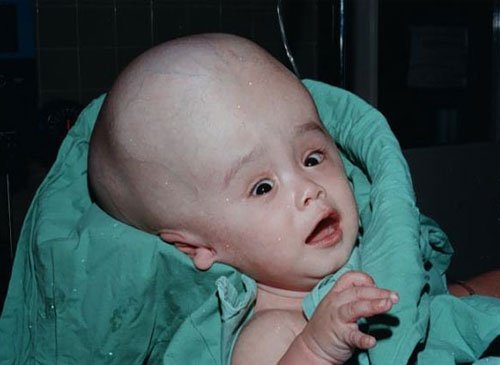
Hydrocephalus Surgery
The neurosurgery team at Sobti Neuro Hospital performs the surgery for hydrocephalus under general anesthesia and it takes less than an hour. There are lots of patients including new borns who have been treated successfully for hydrocephalus. Immediately after surgery, the patient will be taken to the post-anesthesia care unit. They will stay there for close observation for sometime and then be taken to their room. Most patients leave the hospital within 2 to 7 days, depending on their clinical progress.
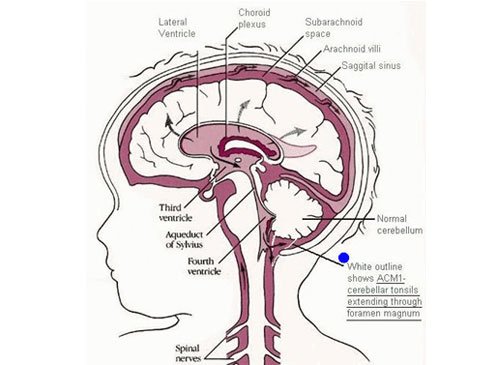
Congenital Brain Abnormalities
Congenital abnormalities, called malformations, are conditions that are present at birth (congenital). There are numerous congenital malformations of the head and spine. Many patients with such congenital abnormalities visit the hospital and they are managed very well surgically or non surgically as required. The purpose of surgery is to correct the physical formation and maximize the functionality for the child to prevent development of neurological deficits. Sobti Neuro and Super Speciality Hospital has successfully treated many cases of children with congenital brain and spine malformations.

Tethered Spinal Cord Syndrome
Tethered spinal cord is a neurological disorder caused by tissue attachments that limit the movement of the spinal cord within the spinal column and cause an abnormal stretching of spinal cord leading to neurological deficits which are generally irreversible. In children, symptoms may include: hairy patches, dimples, or fatty tumours on the lower back, foot and spinal deformities, weakness in the legs, low back pain, chronic urinary incontinence etc. Sobti Hospital does early surgery in such patients having symptoms related to it.

Meningomyelocele Surgery
Myelomeningocele Repair is a surgery to repair birth defects of the spine and spinal membranes. Meningocele and myelomeningocele are types of spina bifida. If the myelomeningocele is not covered by skin or a membrane when your child is born, surgery will happen within 24 to 48 hours after birth to prevent infection. If your child has hydrocephalus, the doctor may put a shunt (plastic tube) in their brain to drain the extra fluid to the stomach. This prevents pressure that could damage the baby’s brain. A lot of new born babies have been treated at Sobti Neuro Hospital for this disease by surgery and the defect is repaired permanently.
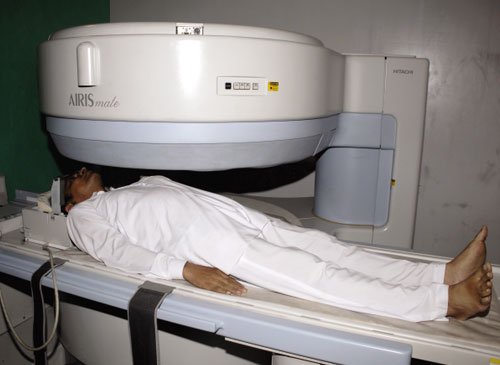
MRI (Open)
Our Open MRI is 3 sided open. Patient don't feel any kind of fear or discomfort during the test. People who get nervous in small places (claustrophobic) may feel better in open MRI. An open MRI is easier to use for people who are very overweight. But not all medical centers have this kind of MRI machine. The open MRI scanner is designed to provide optimal image quality comparable to traditional closed or tunnel MRI scanners. The scanner offers flexibility of positioning to put patients at ease whilst having their MRI scan. 96% of patients who are unable to be scanned in a conventional scanner have been successfully scanned in the Open MRI Scanner.
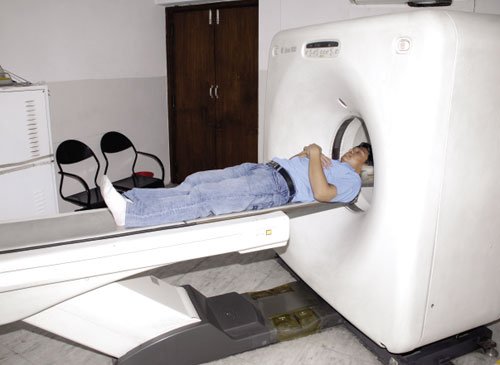
CT Scan
CT scan, is an X-ray procedure that combines many X-ray images with the aid of a computer to generate cross-sectional views and, if needed, three-dimensional images of the internal organs and structures of the body. A CT scan is used to define normal and abnormal structures in the body and/or assist in procedures by helping to accurately guide the placement of instruments or treatments. Our CT Scan offers patients low-dose CT scans. CT scan is used by the radiologists at Sobti Hospital to guide procedures. The images generated during the CT scan are viewed on a computer monitor and printed on film. They can also be transferred to a CD or DVD if the patient demands.
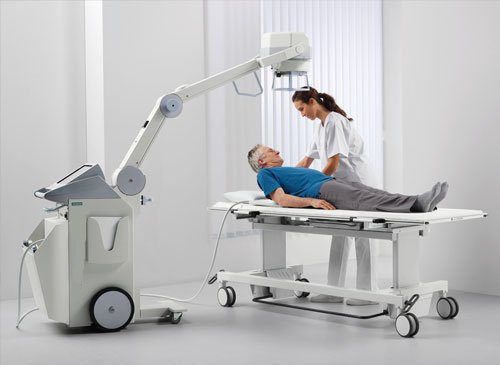
Digital X-Rays
Sobti Hospital does Digital radiography which is a form of X-ray imaging, where digital X-ray sensors are used instead of traditional photographic film. Digital X-Rays is replacement of the former analog methods of detection, with the almost instantaneous development of images on a digital display, instead of the former methods of film and the associated delay in time and chemistry consumption. Advantages include time efficiency through bypassing chemical processing and the ability to digitally transfer and enhance images. Also less radiation can be used to produce an image of similar contrast to conventional radiography.
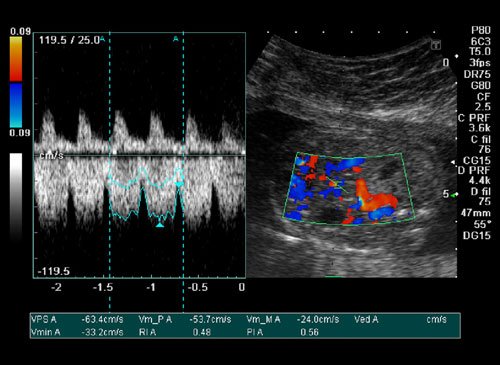
Doppler
Doppler ultrasound is a noninvasive test that can be used to estimate your blood flow through blood vessels. This test may be done as an alternative to more invasive procedures, such as arteriography and venography, which involve injecting dye into the blood vessels so that they show up clearly on X-ray images. It is very helpful to diagnose blood clots, poorly functioning valves in your leg veins, a blocked artery, decreased blood circulation into your legs (peripheral artery disease), narrowing of an artery, such as in your neck (carotid artery stenosis) esp. in patients coming with stroke in the hospital.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a modern surgical technique used in Sobti Hospital in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) as opposed to the larger incisions needed in laparotomy. This surgery makes use of images displayed on TV monitors to magnify the surgical elements. Laparoscopic surgery belong to the broader field of endoscopy. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an open procedure. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions and hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time.
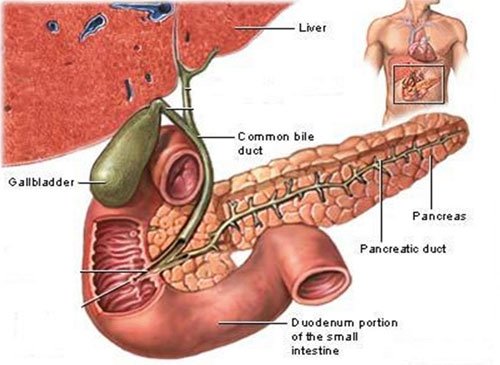
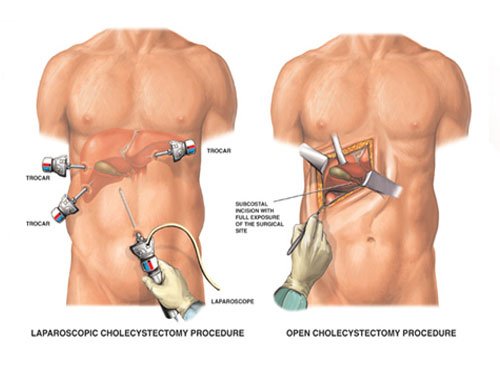
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy is regularly done at Sobti Hospital by the laproscopic surgeon to surgically remove the gallbladder. It is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has now replaced open cholecystectomy as the first-choice of treatment for gallstones and inflammation of the gallbladder unless there are contraindications to the laparoscopic approach. This is because open surgery leaves the patient more prone to infection.
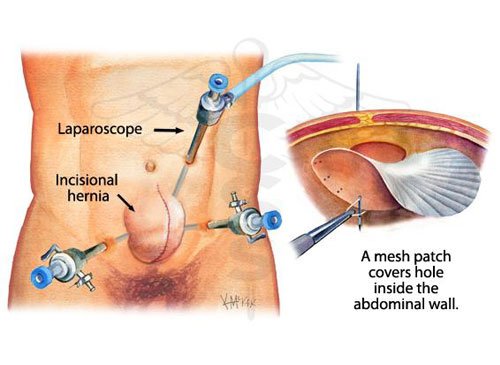
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic hernia repair is similar to other laparoscopic procedures. General anesthesia is given, and a small cut (incision) is made in or just below the navel. The abdomen is inflated with air so that the surgeon can see the abdominal organs. A thin, lighted scope called a laparoscope is inserted through the incision. The instruments to repair the hernia are inserted through other small incisions in the lower abdomen. Mesh is then placed over the defect to reinforce the belly wall.
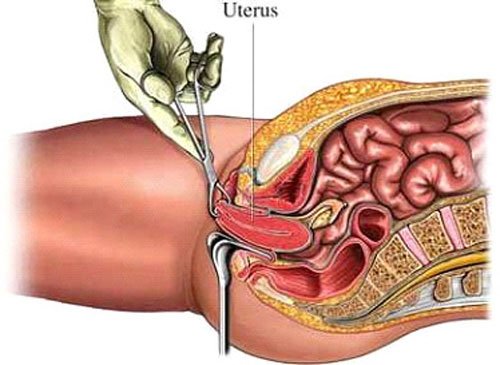
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes and other surrounding structures. Hysterectomy performed at Sobti Hospital, may be total (removing the body, fundus, and cervix of the uterus; often called "complete") or partial (removal of the uterine body while leaving the cervix intact; also called "supracervical"). It is the most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure.
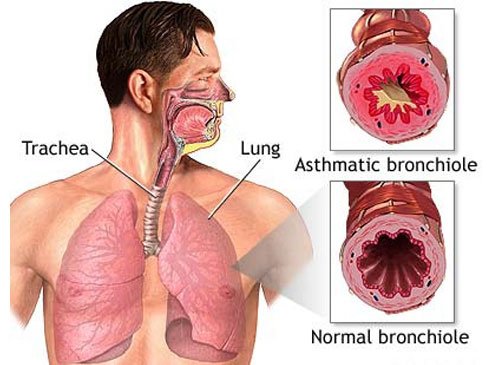
Bronchial Asthma
Bronchial asthma is a chronic lung disorder resulting from the spasmodic contraction of the bronchial muscles. It is most often referred to simply as "asthma". Asthma is treated at Sobti Hospital with bronchial inhalers—including short-term “rescue” inhalers for asthma attacks. Asthma patients are often sensitive to dust, pet dander, mold, and other common irritants. Asthma symptoms can be triggered by exercise, stress, changes in the weather, and respiratory infections.
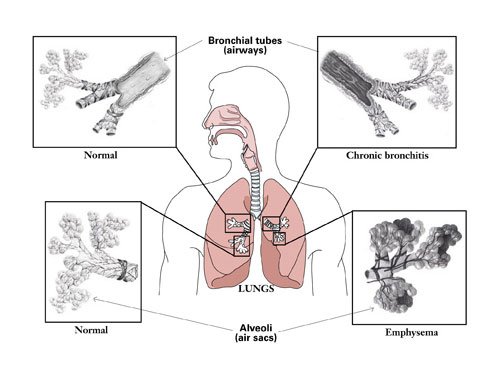
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of obstructive lung disease characterized by chronically poor airflow. It typically worsens over time. The main symptoms include shortness of breath, cough etc. At Sobti Hospital medications used to treat COPD include Inhalers (bronchodilators) to open the airways, inhaled steroids to reduce lung inflammation and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases or during flare-ups, you may need to receive steroids by mouth or intravenously, bronchodilators or oxygen therapy.
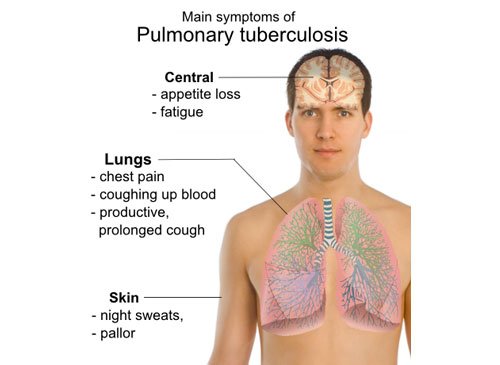
Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB)
TB is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs. You can get TB by breathing in air droplets from a cough or sneeze of an infected person. The goal of treatment is to cure the infection with medicines that fight the TB bacteria. Treatment of active pulmonary TB at Sobti Hospital will always involve a combination of many medicines. Anti-tubercular (ATT) medicines are continued after lab tests to see the amount in which they can be started.
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a group of lung diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the air sacs of the lungs). Prolonged ILD may result in pulmonary fibrosis, but this is not always the case. ILD is not a single disease, but encompasses many different pathological processes. Hence treatment is different for each disease. If a specific occupational exposure cause is found, the person should avoid that environment. If a drug cause is suspected, that drug should be discontinued. Many idiopathic and connective tissue-based causes of ILD are regularly treated at Sobti Hospital with corticosteroids, such as prednisolone.
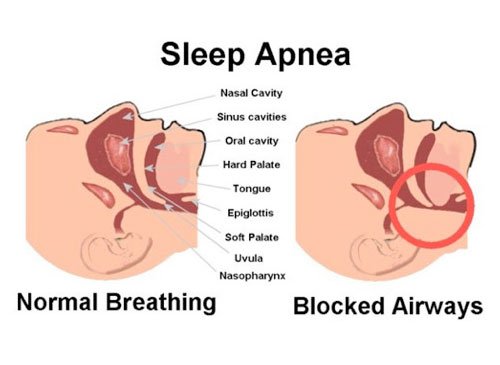
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea and is caused by obstruction of the upper airway. It is characterized by repetitive pauses in breathing during sleep, despite the effort to breathe. Nasal surgery is done in patients with nasal obstruction which reduces airway pressure and complicates OSA. OSA in children is sometimes due to chronically enlarged tonsils and adenoids. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy is curative. Even in these extreme cases, the surgery at Sobti Hospital tends to cure not only the apnea and upper airway obstruction, but allows normal subsequent growth and development.
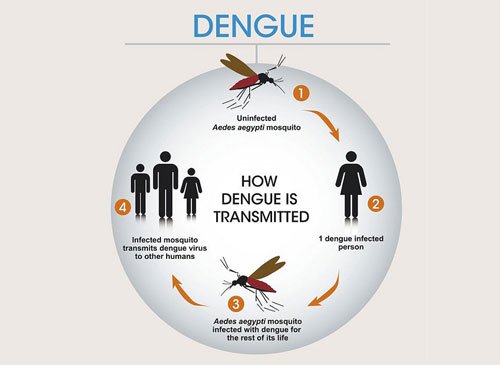
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle and joint pains. Treatment at Sobti Hospital starts with intravenous hydration, which is typically needed for one or two days. The rate of fluid administration is titrated to a urinary output of 0.5–1 mL/kg/h, stable vital signs and normalization of hematocrit. The smallest amount of fluid required to achieve this is recommended. Invasive medical procedures at Sobti Hospital such as nasogastric intubation, intramuscular injections and arterial punctures are done as required.
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis or infectious diarrhea is a medical condition characterized by inflammation ("-itis") of the gastrointestinal tract resulting in some combination of diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain and cramping. Gastroenteritis is typically diagnosed clinically at Sobti Hospital, based on a person's signs and symptoms. Determining the exact cause is usually not needed as it does not alter management of the condition. However, stool cultures are performed in those with blood in the stool, those who might have been exposed to food poisoning.
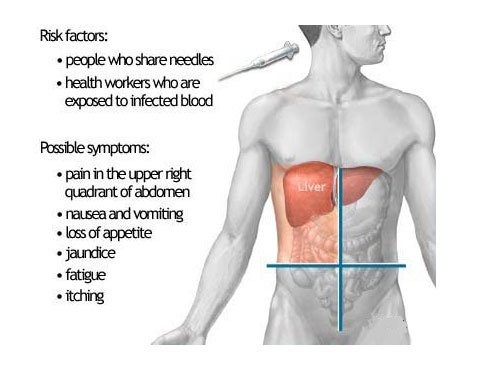
Chronic Liver Disease
Chronic liver disease in the clinical context is a disease process of the liver that involves a process of progressive destruction and regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Symptoms of liver diseases include weakness and fatigue, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, and yellow discoloration of the skin (jaundice). The treatment of chronic liver disease at Sobti Hospital depends on the cause. While some conditions may be treated with medications, others may require surgery or a transplant. Transplant is required when the liver fails and there is no other alternative.
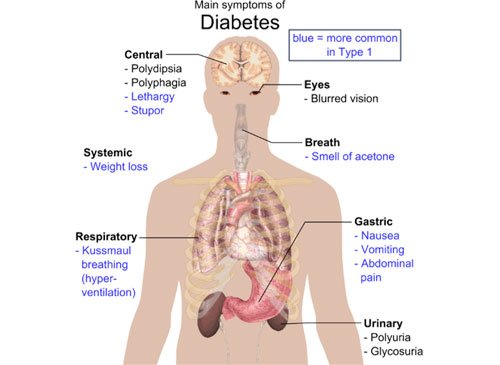
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus (DM) or simply diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar. This high blood sugar produces the symptoms of frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased hunger. Untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. Acute complications include diabetic ketoacidosis and nonketotic hyperosmolar coma. Serious long-term complications include heart disease, kidney failure, and damage to the eyes. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or because cells of the body do not respond properly to the insulin that is produced.
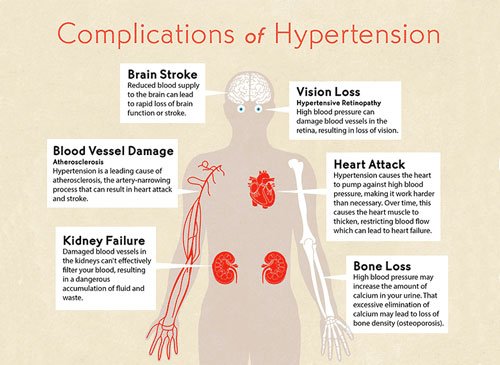
Hypertension
Hypertension (HTN) or high blood pressure, sometimes called arterial hypertension, is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. Blood pressure is summarised by two measurements, systolic and diastolic, which depend on whether the heart muscle is contracting (systole) or relaxed between beats (diastole). This equals the maximum and minimum pressure, respectively. Normal blood pressure at rest is within the range of 100–140mmHg systolic (top reading) and 60–90mmHg diastolic.
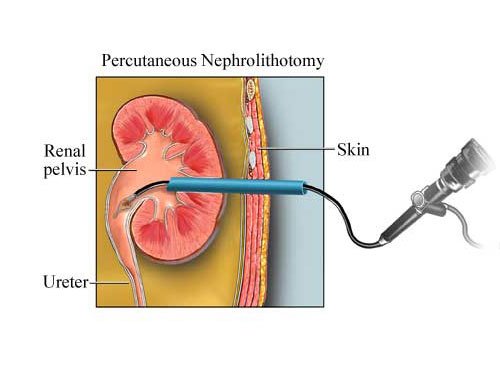
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a surgical procedure to remove stones from the kidney by a small puncture wound (up to about 1 cm) through the skin. It is most suitable to remove stones of more than 2 cm in size. It is usually done at Sobti Hospital under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. A Retrograde pyelogram is done to locate the stone in the kidney. With a small 1 centimeter incision in the loin, the Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCN) needle is passed into the pelvis of the kidney.
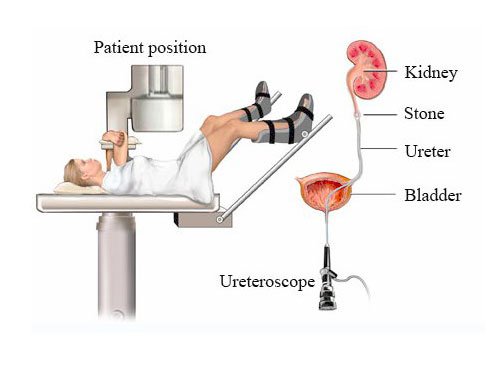
Ureteroscopy
Ureteroscopy is an examination of the upper urinary tract, regularly performed at Sobti Hospital with an ureteroscope that is passed through the urethra, bladder, and then directly into the ureter usually lower 2/3rd of the ureter is accessible by this procedure. The procedure is useful in the diagnosis and the treatment of disorders such as kidney stones. Smaller stones in bladder or lower ureter can be removed in one piece, while bigger ones are usually broken before removal during ureteroscopy.
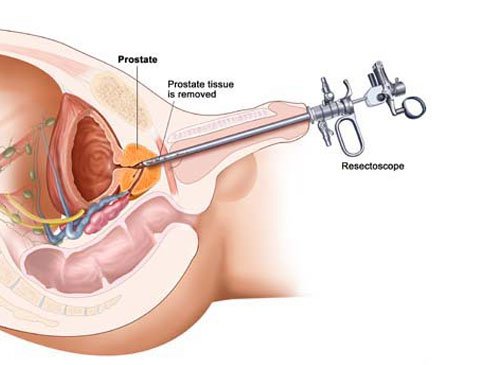
Transurethral resection of bladder tumour
Transurethral resection (TUR) of the bladder is a surgical procedure that is used both to diagnose bladder cancer and to remove cancerous tissue from the bladder. General anesthesia or spinal anesthesia is often used. During TUR surgery at Sobti Hospital, a cystoscope is passed into the bladder through the urethra. A tool called a resectoscope is used to remove the cancer for biopsy and to burn away any remaining cancer cells. Following surgery, a catheter may be placed in the urethra to help stop bleeding and to prevent blockage of the urethra. When the bleeding has stopped, the catheter is removed. You may need to stay in the hospital for 1 to 4 days.
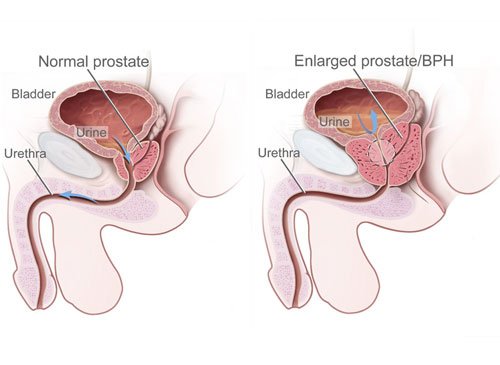
Transurethral Prostatic Resection (TUPR)
Transurethral resection of the prostate is performed at Sobti Hospital by experienced urologist. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It is performed by visualising the prostate through the urethra and removing tissue by electrocautery or sharp dissection. This is considered the most effective treatment for BPH. This procedure is done at Sobti Hospital with spinal or general anaesthesia. A triple lumen catheter is inserted through the urethra to irrigate and drain the bladder after the surgical procedure is complete. Outcome is excellent for more than 90% of BPH patients.
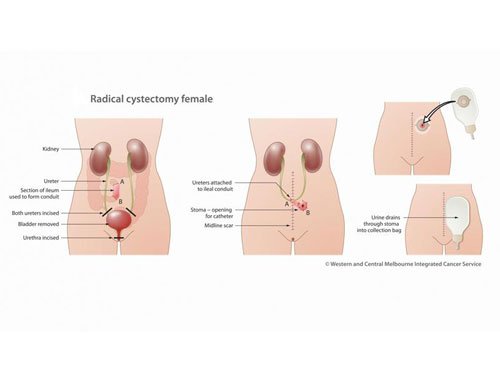
Cystectomy
Cystectomy is a medical term for surgical removal of all or part of the urinary bladder. The most common condition warranting removal of the urinary bladder is bladder cancer. After the bladder has been removed, an Ileal conduit urinary diversion is necessary. An alternative to this method is to construct a pouch from a section of ileum or colon, which can act as a form of replacement bladder, storing urine until the patient desires to release it, which can be achieved by either abdominal straining or self catheterisation.
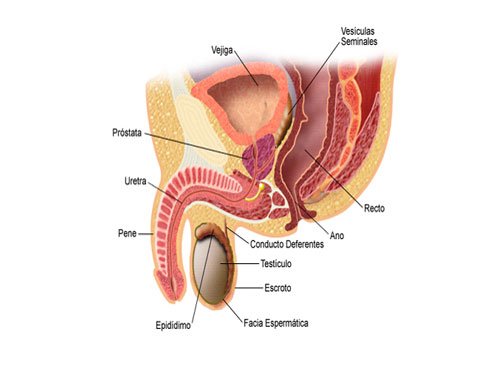
Andrology
Andrology is the medical specialty that deals with male health, particularly relating to the problems of the male reproductive system and urological problems that are unique to men. It is also known as "The science of Men". It is the counterpart to gynaecology, which deals with medical issues which are specific to the female reproductive system. Male-specific medical and surgical procedures at Sobti Hospital include vasectomy and vasovasostomy (one of the vasectomy reversal procedures) as well as intervention to deal with male genitourinary disorders such as epispadias, erectile dysfunction, frenulum breve etc.