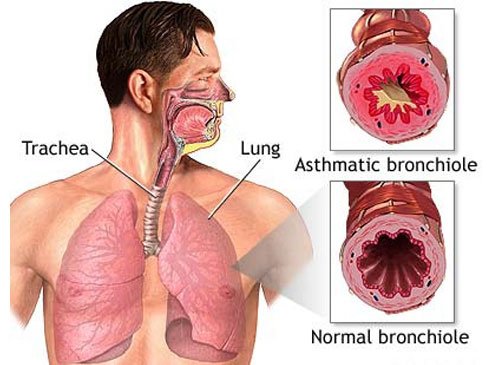
Bronchial Asthma
Bronchial asthma is a chronic lung disorder resulting from the spasmodic contraction of the bronchial muscles. It is most often referred to simply as "asthma". Asthma is treated at Sobti Hospital with bronchial inhalers—including short-term “rescue” inhalers for asthma attacks. Asthma patients are often sensitive to dust, pet dander, mold, and other common irritants. Asthma symptoms can be triggered by exercise, stress, changes in the weather, and respiratory infections.
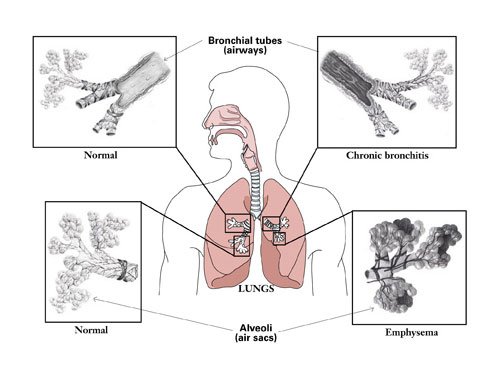
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of obstructive lung disease characterized by chronically poor airflow. It typically worsens over time. The main symptoms include shortness of breath, cough etc. At Sobti Hospital medications used to treat COPD include Inhalers (bronchodilators) to open the airways, inhaled steroids to reduce lung inflammation and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases or during flare-ups, you may need to receive steroids by mouth or intravenously, bronchodilators or oxygen therapy.
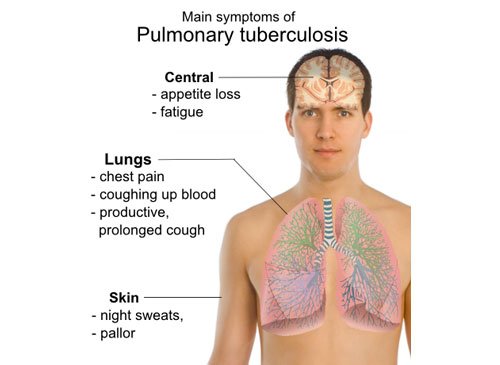
Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB)
TB is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs. You can get TB by breathing in air droplets from a cough or sneeze of an infected person. The goal of treatment is to cure the infection with medicines that fight the TB bacteria. Treatment of active pulmonary TB at Sobti Hospital will always involve a combination of many medicines. Anti-tubercular (ATT) medicines are continued after lab tests to see the amount in which they can be started.
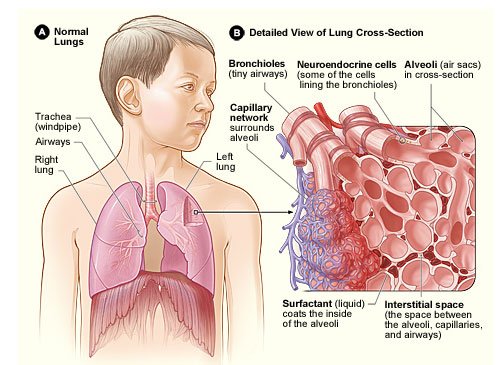
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a group of lung diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the air sacs of the lungs). Prolonged ILD may result in pulmonary fibrosis, but this is not always the case. ILD is not a single disease, but encompasses many different pathological processes. Hence treatment is different for each disease. If a specific occupational exposure cause is found, the person should avoid that environment. If a drug cause is suspected, that drug should be discontinued. Many idiopathic and connective tissue-based causes of ILD are regularly treated at Sobti Hospital with corticosteroids, such as prednisolone.
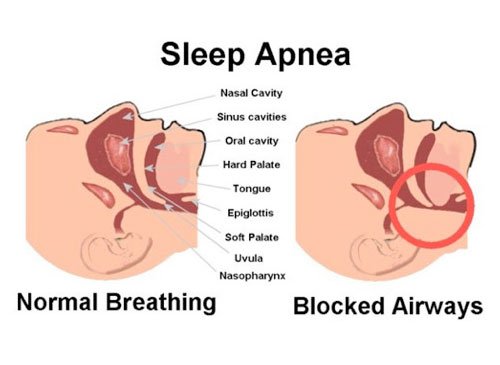
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea and is caused by obstruction of the upper airway. It is characterized by repetitive pauses in breathing during sleep, despite the effort to breathe. Nasal surgery is done in patients with nasal obstruction which reduces airway pressure and complicates OSA. OSA in children is sometimes due to chronically enlarged tonsils and adenoids. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy is curative. Even in these extreme cases, the surgery at Sobti Hospital tends to cure not only the apnea and upper airway obstruction, but allows normal subsequent growth and development.
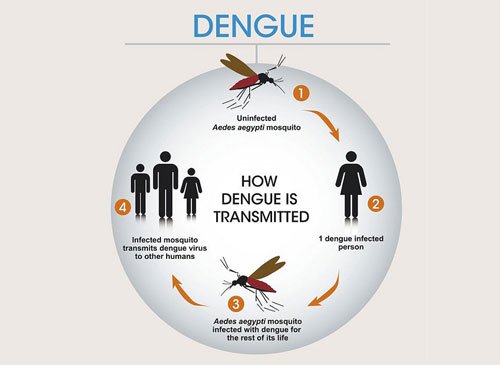
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle and joint pains. Treatment at Sobti Hospital starts with intravenous hydration, which is typically needed for one or two days. The rate of fluid administration is titrated to a urinary output of 0.5–1 mL/kg/h, stable vital signs and normalization of hematocrit. The smallest amount of fluid required to achieve this is recommended. Invasive medical procedures at Sobti Hospital such as nasogastric intubation, intramuscular injections and arterial punctures are done as required.
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis or infectious diarrhea is a medical condition characterized by inflammation ("-itis") of the gastrointestinal tract resulting in some combination of diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain and cramping. Gastroenteritis is typically diagnosed clinically at Sobti Hospital, based on a person's signs and symptoms. Determining the exact cause is usually not needed as it does not alter management of the condition. However, stool cultures are performed in those with blood in the stool, those who might have been exposed to food poisoning.
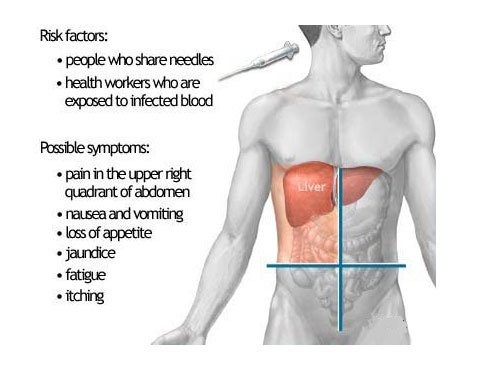
Chronic Liver Disease
Chronic liver disease in the clinical context is a disease process of the liver that involves a process of progressive destruction and regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Symptoms of liver diseases include weakness and fatigue, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, and yellow discoloration of the skin (jaundice). The treatment of chronic liver disease at Sobti Hospital depends on the cause. While some conditions may be treated with medications, others may require surgery or a transplant. Transplant is required when the liver fails and there is no other alternative.
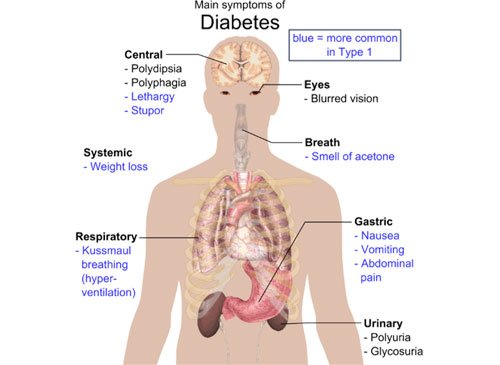
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus (DM) or simply diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar. This high blood sugar produces the symptoms of frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased hunger. Untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. Acute complications include diabetic ketoacidosis and nonketotic hyperosmolar coma. Serious long-term complications include heart disease, kidney failure, and damage to the eyes. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or because cells of the body do not respond properly to the insulin that is produced.
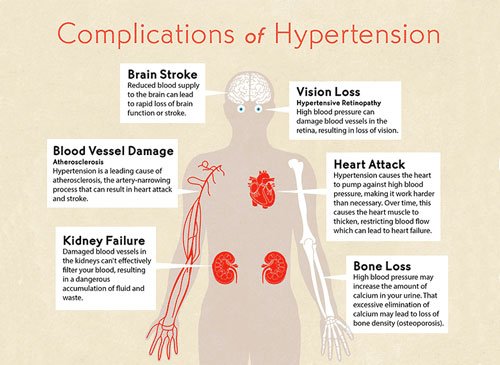
Hypertension
Hypertension (HTN) or high blood pressure, sometimes called arterial hypertension, is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. Blood pressure is summarised by two measurements, systolic and diastolic, which depend on whether the heart muscle is contracting (systole) or relaxed between beats (diastole). This equals the maximum and minimum pressure, respectively. Normal blood pressure at rest is within the range of 100–140mmHg systolic (top reading) and 60–90mmHg diastolic.