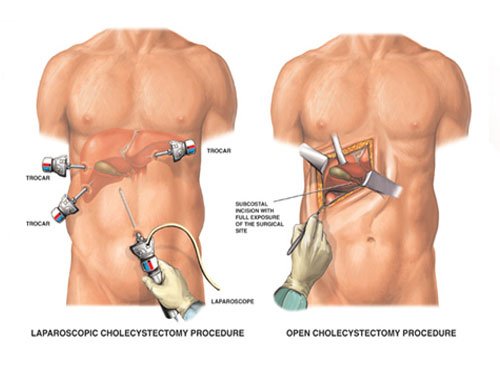
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a modern surgical technique used in Sobti Hospital in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) as opposed to the larger incisions needed in laparotomy. This surgery makes use of images displayed on TV monitors to magnify the surgical elements. Laparoscopic surgery belong to the broader field of endoscopy. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an open procedure. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions and hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time.
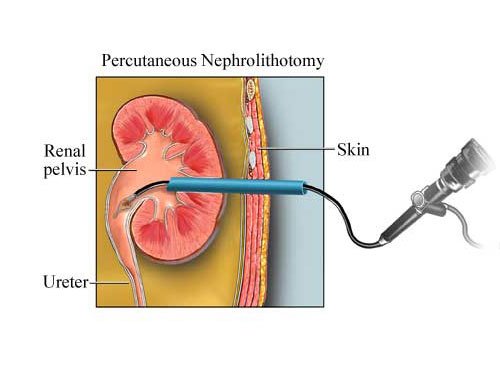
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a surgical procedure to remove stones from the kidney by a small puncture wound (up to about 1 cm) through the skin. It is most suitable to remove stones of more than 2 cm in size. It is usually done at Sobti Hospital under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. A Retrograde pyelogram is done to locate the stone in the kidney. With a small 1 centimeter incision in the loin, the Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCN) needle is passed into the pelvis of the kidney.
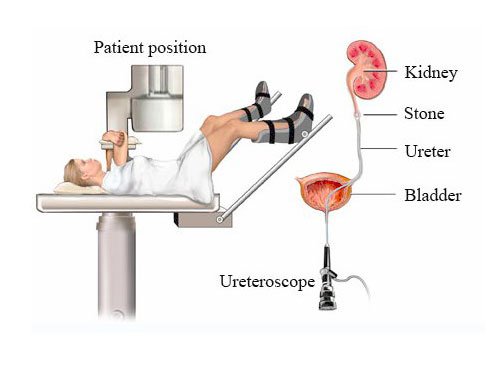
Ureteroscopy
Ureteroscopy is an examination of the upper urinary tract, regularly performed at Sobti Hospital with an ureteroscope that is passed through the urethra, bladder, and then directly into the ureter usually lower 2/3rd of the ureter is accessible by this procedure. The procedure is useful in the diagnosis and the treatment of disorders such as kidney stones. Smaller stones in bladder or lower ureter can be removed in one piece, while bigger ones are usually broken before removal during ureteroscopy.
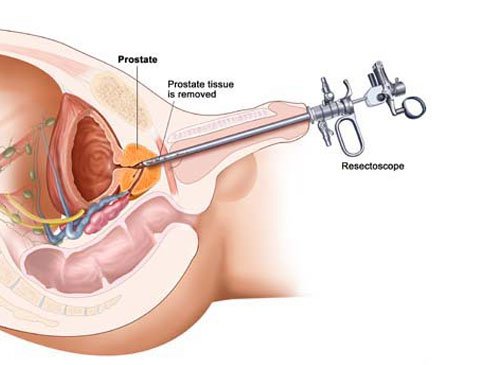
Transurethral resection of bladder tumour
Transurethral resection (TUR) of the bladder is a surgical procedure that is used both to diagnose bladder cancer and to remove cancerous tissue from the bladder. General anesthesia or spinal anesthesia is often used. During TUR surgery at Sobti Hospital, a cystoscope is passed into the bladder through the urethra. A tool called a resectoscope is used to remove the cancer for biopsy and to burn away any remaining cancer cells. Following surgery, a catheter may be placed in the urethra to help stop bleeding and to prevent blockage of the urethra. When the bleeding has stopped, the catheter is removed. You may need to stay in the hospital for 1 to 4 days.
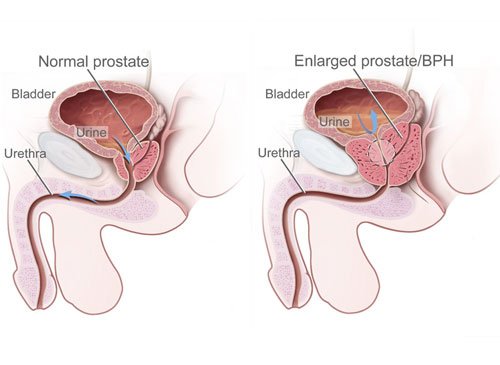
Transurethral Prostatic Resection (TUPR)
Transurethral resection of the prostate is performed at Sobti Hospital by experienced urologist. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It is performed by visualising the prostate through the urethra and removing tissue by electrocautery or sharp dissection. This is considered the most effective treatment for BPH. This procedure is done at Sobti Hospital with spinal or general anaesthesia. A triple lumen catheter is inserted through the urethra to irrigate and drain the bladder after the surgical procedure is complete. Outcome is excellent for more than 90% of BPH patients.
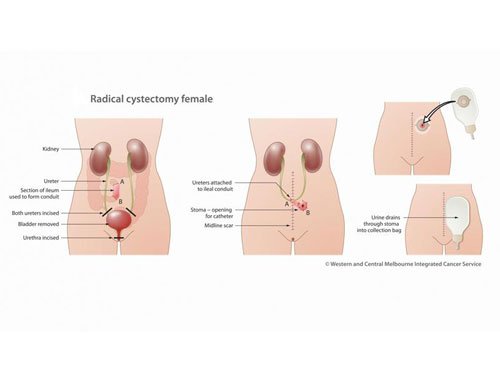
Cystectomy
Cystectomy is a medical term for surgical removal of all or part of the urinary bladder. The most common condition warranting removal of the urinary bladder is bladder cancer. After the bladder has been removed, an Ileal conduit urinary diversion is necessary. An alternative to this method is to construct a pouch from a section of ileum or colon, which can act as a form of replacement bladder, storing urine until the patient desires to release it, which can be achieved by either abdominal straining or self catheterisation.
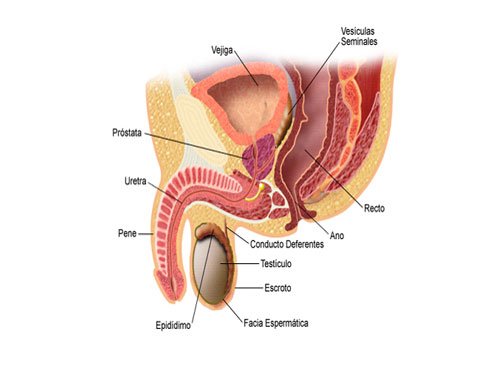
Andrology
Andrology is the medical specialty that deals with male health, particularly relating to the problems of the male reproductive system and urological problems that are unique to men. It is also known as "The science of Men". It is the counterpart to gynaecology, which deals with medical issues which are specific to the female reproductive system. Male-specific medical and surgical procedures at Sobti Hospital include vasectomy and vasovasostomy (one of the vasectomy reversal procedures) as well as intervention to deal with male genitourinary disorders such as epispadias, erectile dysfunction, frenulum breve etc.